文章目录
- 一、环境部署
- 二、导入原图
- 2.1 使用vit_s14的模型
- 三、使用其他模型
- 3.1 使用vit_b14的模型
- 3.2 使用vit_l14的模型
- 3.3 使用vit_g14的模型
一、环境部署
!git clone https://ghproxy.com/https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2.git
输出为:
Cloning into 'dinov2'... remote: Enumerating objects: 141, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (96/96), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (74/74), done. 71% (53/74) remote: Total 141 (delta 40), reused 31 (delta 22), pack-reused 45 Receiving objects: 100% (141/141), 101.01 KiB | 348.00 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (42/42), done.
命令是一个Git命令,用于克隆(Clone)名为"dinov2"的存储库。它使用了一个名为"ghproxy.com"的代理,用于加速GitHub的克隆操作。
!pip install -r /kaggle/working/dinov2/requirements.txt
!pip install scikit-learn -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
二、导入原图
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.image as mpimg image = mpimg.imread('/kaggle/input/demo-image/1 (4).png') plt.imshow(image) plt.axis('off') plt.show() # 输出图像尺寸 print("图像尺寸:{} x {} x {}".format(image.shape[0], image.shape[1], image.shape[2]))图像尺寸:1376 x 920 x 3
我们需要切换为output的路径:
import os input_path = "/kaggle/working/dinov2" os.chdir(input_path)
2.1 使用vit_s14的模型
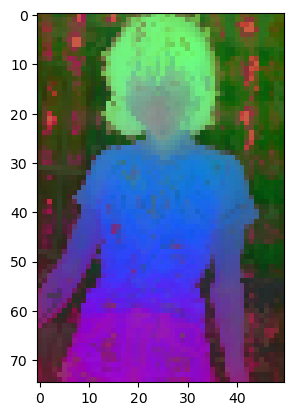
import torch import torchvision.transforms as T import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import matplotlib.image as mpimg from PIL import Image from sklearn.decomposition import PCA import matplotlib patch_h = 75 patch_w = 50 feat_dim = 384 transform = T.Compose([ T.GaussianBlur(9, sigma=(0.1, 2.0)), T.Resize((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.CenterCrop((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)), ]) dinov2_vits14 = torch.hub.load('', 'dinov2_vits14',source='local').cuda() features = torch.zeros(4, patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim) imgs_tensor = torch.zeros(4, 3, patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14).cuda() img_path = f'/kaggle/input/demo-image/1 (4).png' img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB') imgs_tensor[0] = transform(img)[:3] with torch.no_grad(): features_dict = dinov2_vits14.forward_features(imgs_tensor) features = features_dict['x_norm_patchtokens'] features = features.reshape(4 * patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim).cpu() pca = PCA(n_components=3) pca.fit(features) pca_features = pca.transform(features) pca_features[:, 0] = (pca_features[:, 0] - pca_features[:, 0].min()) / (pca_features[:, 0].max() - pca_features[:, 0].min()) pca_features_fg = pca_features[:, 0] > 0.3 pca_features_bg = ~pca_features_fg b = np.where(pca_features_bg) pca.fit(features[pca_features_fg]) pca_features_rem = pca.transform(features[pca_features_fg]) for i in range(3): pca_features_rem[:, i] = (pca_features_rem[:, i] - pca_features_rem[:, i].min()) / (pca_features_rem[:, i].max() - pca_features_rem[:, i].min()) # transform using mean and std, I personally found this transformation gives a better visualization # pca_features_rem[:, i] = (pca_features_rem[:, i] - pca_features_rem[:, i].mean()) / (pca_features_rem[:, i].std() ** 2) + 0.5 pca_features_rgb = pca_features.copy() pca_features_rgb[pca_features_fg] = pca_features_rem pca_features_rgb[b] = 0 pca_features_rgb = pca_features_rgb.reshape(4, patch_h, patch_w, 3) plt.imshow(pca_features_rgb[0][...,::-1]) plt.savefig('features.png') plt.show() plt.close()以下是代码的逐行中文解读:
import torch import torchvision.transforms as T import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import matplotlib.image as mpimg from PIL import Image from sklearn.decomposition import PCA import matplotlib # 设置补丁(patch)的高度和宽度 patch_h = 75 patch_w = 50 # 特征维度 feat_dim = 384 # 定义图像转换操作 transform = T.Compose([ T.GaussianBlur(9, sigma=(0.1, 2.0)), # 高斯模糊 T.Resize((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), # 调整图像大小 T.CenterCrop((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), # 中心裁剪 T.ToTensor(), # 转换为张量 T.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)), # 标准化 ]) # 使用torch.hub加载dinov2_vits14模型并移***CUDA设备 dinov2_vits14 = torch.hub.load('', 'dinov2_vits14', source='local').cuda() # 创建用于存储特征和图像张量的零张量 features = torch.zeros(4, patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim) imgs_tensor = torch.zeros(4, 3, patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14).cuda() # 图像路径 img_path = f'/kaggle/input/demo-image/1 (4).png' # 打开图像并转换为RGB模式 img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB') # 对图像进行转换操作,并将其存储在imgs_tensor的***个位置 imgs_tensor[0] = transform(img)[:3] # 禁用梯度计算 with torch.no_grad(): # 将图像张量传递给dinov2_vits14模型获取特征 features_dict = dinov2_vits14.forward_features(imgs_tensor) features = features_dict['x_norm_patchtokens'] # 重塑特征形状为(4 * patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim) features = features.reshape(4 * patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim).cpu() # 创建PCA对象并拟合特征 pca = PCA(n_components=3) pca.fit(features) # 对PCA转换后的特征进行归一化处理 pca_features = pca.transform(features) pca_features[:, 0] = (pca_features[:, 0] - pca_features[:, 0].min()) / (pca_features[:, 0].max() - pca_features[:, 0].min()) # 根据阈值进行前景和背景的区分 pca_features_fg = pca_features[:, 0] > 0.3 pca_features_bg = ~pca_features_fg # 查找背景特征的索引 b = np.where(pca_features_bg) # 对前景特征再次进行PCA转换 pca.fit(features[pca_features_fg]) pca_features_rem = pca.transform(features[pca_features_fg]) # 对前景特征进行归一化处理 for i in range(3): pca_features_rem[:, i] = (pca_features_rem[:, i] - pca_features_rem[:, i].min()) / (pca_features_rem[:, i].max() - pca_features_rem[:, i].min()) # 使用均值和标准差进行转换,个人发现这种转换方式可以得到更好的可视化效果 # pca_features_rem[:, i] = (pca_features_rem[:, i] - pca_features_rem[:, i].mean()) / (pca_features_rem[:, i].std() ** 2) + 0.5 # 创建RGB特征数组 pca_features_rgb = pca_features.copy() # 替换前景特征为转换后的特征 pca_features_rgb[pca_features_fg] = pca_features_rem # 将背景特征设置为0 pca_features_rgb[b] = 0 # 重塑特征形状为(4, patch_h, patch_w, 3) pca_features_rgb = pca_features_rgb.reshape(4, patch_h, patch_w, 3) # 显示***个图像的RGB特征 plt.imshow(pca_features_rgb[0][...,::-1]) plt.savefig('features.png') plt.show() plt.close()这段代码的功能是对给定的图像进行一系列处理和特征提取,并使用PCA对特征进行降维。然后,根据特定阈值对前景和背景进行区分,***后将特征可视化为RGB图像。请注意,其中的具体数值和路径可能需要根据您的实际数据和环境进行调整。
print(features) print(features.shape)
我们的输出结果为:
tensor([[-1.3500, -4.8793, -1.4393, ..., 2.3347, 1.6834, -2.9632], [-0.4650, -6.4163, -1.5503, ..., 2.2055, 2.5527, -3.2553], [-0.6371, -6.2615, -0.7516, ..., 3.1827, 2.3861, -2.6838], ..., [ 1.9385, 0.0726, -0.5395, ..., 0.3876, -1.4914, -4.5422], [ 1.6399, -0.0860, 0.4701, ..., 1.0180, -0.8897, -5.2614], [ 1.6084, -0.0669, 0.7341, ..., 1.0633, -0.9713, -5.3548]]) torch.Size([15000, 384])降维后的特征为:
print(pca_features) print(pca_features.shape)
输出的结果为:
[[ 0.81004055 2.458559 12.11051576] [ 0.79562888 5.65071716 10.84007045] [ 0.82050109 5.55007889 9.05274001] ... [ 0.27618588 -18.96898667 19.48198916] [ 0.31861323 -12.21414371 14.19802898] [ 0.34356016 -10.82144825 13.74648131]] (15000, 3)
features_dict
我们看一下字典的构成:
{'x_norm_clstoken': tensor([[ 2.2549, -1.5661, 4.4978, ..., 1.4984, -5.8642, -0.8560], [ 1.8816, 2.4343, 1.4931, ..., -1.3401, -2.5460, 1.3967], [ 1.8816, 2.4343, 1.4931, ..., -1.3401, -2.5460, 1.3967], [ 1.8816, 2.4343, 1.4931, ..., -1.3401, -2.5460, 1.3967]], device='cuda:0'), 'x_norm_patchtokens': tensor([[[-1.3500, -4.8793, -1.4393, ..., 2.3347, 1.6834, -2.9632], [-0.4650, -6.4163, -1.5503, ..., 2.2055, 2.5527, -3.2553], [-0.6371, -6.2615, -0.7516, ..., 3.1827, 2.3861, -2.6838], ..., [-0.8778, -0.0251, -0.2867, ..., 4.7801, -2.0887, -4.5910], [-1.2309, 0.2852, 0.7693, ..., 5.0635, -1.1529, -6.0175], [-1.7551, 1.1333, -0.0898, ..., 4.1885, -3.3197, -5.7227]], [[ 0.9131, -4.9736, -0.6238, ..., 0.2835, -0.3494, -0.4916], [ 1.0967, -6.0392, -0.7900, ..., 0.2323, 0.0510, 0.0176], [ 1.3852, -5.8056, -1.2573, ..., 0.0549, -0.3270, -0.4510], ..., [ 1.9385, 0.0726, -0.5395, ..., 0.3877, -1.4914, -4.5422], [ 1.6399, -0.0860, 0.4701, ..., 1.0180, -0.8897, -5.2614], [ 1.6084, -0.0669, 0.7341, ..., 1.0633, -0.9713, -5.3548]], [[ 0.9131, -4.9736, -0.6238, ..., 0.2835, -0.3494, -0.4916], [ 1.0967, -6.0392, -0.7900, ..., 0.2323, 0.0510, 0.0176], [ 1.3852, -5.8056, -1.2573, ..., 0.0549, -0.3270, -0.4510], ..., [ 1.9385, 0.0726, -0.5395, ..., 0.3877, -1.4914, -4.5422], [ 1.6399, -0.0860, 0.4701, ..., 1.0180, -0.8897, -5.2614], [ 1.6085, -0.0669, 0.7341, ..., 1.0633, -0.9713, -5.3548]], [[ 0.9131, -4.9736, -0.6238, ..., 0.2835, -0.3494, -0.4916], [ 1.0967, -6.0392, -0.7900, ..., 0.2323, 0.0510, 0.0176], [ 1.3852, -5.8056, -1.2573, ..., 0.0549, -0.3270, -0.4511], ..., [ 1.9385, 0.0726, -0.5395, ..., 0.3876, -1.4914, -4.5422], [ 1.6399, -0.0860, 0.4701, ..., 1.0180, -0.8897, -5.2614], [ 1.6084, -0.0669, 0.7341, ..., 1.0633, -0.9713, -5.3548]]], device='cuda:0'), 'x_prenorm': tensor([[[ 4.7546e-01, -3.4794e-02, 1.1905e+00, ..., 3.3896e-01, -1.2591e+00, -8.1724e-03], [-5.2994e-01, -3.0311e-01, -2.0162e-01, ..., 9.4372e-01, 8.7399e-01, -3.2527e-01], [-1.5728e-01, -3.9359e-01, -2.1482e-01, ..., 9.0485e-01, 1.2325e+00, -3.3923e-01], ..., [-4.9091e-01, 1.1081e-02, 1.9814e-01, ..., 2.0630e+00, -8.5562e-01, -7.6588e-01], [-6.0861e-01, 5.2204e-02, 6.6299e-01, ..., 2.1127e+00, -3.8590e-01, -9.7335e-01], [-9.3785e-01, 1.2485e-01, 3.0359e-01, ..., 1.9137e+00, -1.5223e+00, -1.0352e+00]], [[ 4.4059e-01, 1.4807e-01, 5.9425e-01, ..., -3.4851e-01, -6.1687e-01, 2.0463e-01], [ 3.1511e-01, -3.3073e-01, 9.0955e-02, ..., 1.3627e-01, 1.8562e-02, 4.2850e-02], [ 3.8695e-01, -4.1345e-01, 2.8734e-02, ..., 1.1916e-01, 1.8061e-01, 1.2469e-01], ..., [ 6.3855e-01, 1.9967e-03, 5.6187e-02, ..., 1.0780e-01, -5.0606e-01, -6.6095e-01], [ 5.6617e-01, 4.9071e-03, 4.8375e-01, ..., 3.7527e-01, -2.6194e-01, -7.9524e-01], [ 5.6790e-01, 1.4408e-02, 6.0538e-01, ..., 4.0537e-01, -2.9182e-01, -8.1226e-01]], [[ 4.4059e-01, 1.4807e-01, 5.9424e-01, ..., -3.4851e-01, -6.1687e-01, 2.0463e-01], [ 3.1511e-01, -3.3073e-01, 9.0957e-02, ..., 1.3627e-01, 1.8564e-02, 4.2850e-02], [ 3.8695e-01, -4.1345e-01, 2.8733e-02, ..., 1.1916e-01, 1.8061e-01, 1.2469e-01], ..., [ 6.3855e-01, 1.9971e-03, 5.6186e-02, ..., 1.0780e-01, -5.0606e-01, -6.6095e-01], [ 5.6617e-01, 4.9067e-03, 4.8375e-01, ..., 3.7527e-01, -2.6194e-01, -7.9524e-01], [ 5.6790e-01, 1.4408e-02, 6.0538e-01, ..., 4.0536e-01, -2.9182e-01, -8.1226e-01]], [[ 4.4059e-01, 1.4807e-01, 5.9424e-01, ..., -3.4851e-01, -6.1687e-01, 2.0463e-01], [ 3.1511e-01, -3.3073e-01, 9.0956e-02, ..., 1.3627e-01, 1.8562e-02, 4.2849e-02], [ 3.8695e-01, -4.1344e-01, 2.8735e-02, ..., 1.1916e-01, 1.8061e-01, 1.2469e-01], ..., [ 6.3855e-01, 1.9964e-03, 5.6189e-02, ..., 1.0780e-01, -5.0607e-01, -6.6095e-01], [ 5.6617e-01, 4.9066e-03, 4.8375e-01, ..., 3.7527e-01, -2.6194e-01, -7.9524e-01], [ 5.6790e-01, 1.4408e-02, 6.0538e-01, ..., 4.0537e-01, -2.9182e-01, -8.1226e-01]]], device='cuda:0'), 'masks': None}我们换一种可视化的方法:
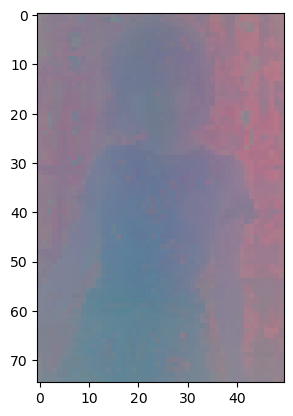
patch_h = 75 patch_w = 50 feat_dim = 384 transform = T.Compose([ T.GaussianBlur(9, sigma=(0.1, 2.0)), T.Resize((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.CenterCrop((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)), ]) dinov2_vits14 = torch.hub.load('', 'dinov2_vits14',source='local').cuda() features = torch.zeros(4, patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim) imgs_tensor = torch.zeros(4, 3, patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14).cuda() img_path = f'/kaggle/input/demo-image/1 (4).png' img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB') imgs_tensor[0] = transform(img)[:3] with torch.no_grad(): features_dict = dinov2_vits14.forward_features(imgs_tensor) features = features_dict['x_norm_patchtokens'] features = features.reshape(4 * patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim).cpu() pca = PCA(n_components=3) pca.fit(features) pca_features = pca.transform(features) pca_features[:, 0] = (pca_features[:, 0] - pca_features[:, 0].min()) / (pca_features[:, 0].max() - pca_features[:, 0].min()) pca_features_fg = pca_features[:, 0] > 0.3 pca_features_bg = ~pca_features_fg b = np.where(pca_features_bg) pca.fit(features[pca_features_fg]) pca_features_rem = pca.transform(features[pca_features_fg]) for i in range(3): # transform using mean and std, I personally found this transformation gives a better visualization pca_features_rem[:, i] = (pca_features_rem[:, i] - pca_features_rem[:, i].mean()) / (pca_features_rem[:, i].std() ** 2) + 0.5 pca_features_rgb = pca_features.copy() pca_features_rgb[pca_features_fg] = pca_features_rem pca_features_rgb[b] = 0 pca_features_rgb = pca_features_rgb.reshape(4, patch_h, patch_w, 3) plt.imshow(pca_features_rgb[0][...,::-1]) plt.savefig('features.png') plt.show() plt.close()三、使用其他模型
3.1 使用vit_b14的模型
patch_h = 75 patch_w = 50 feat_dim = 768 transform = T.Compose([ T.GaussianBlur(9, sigma=(0.1, 2.0)), T.Resize((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.CenterCrop((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)), ]) dinov2_vitb14 = torch.hub.load('', 'dinov2_vitb14',source='local').cuda() features = torch.zeros(4, patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim) imgs_tensor = torch.zeros(4, 3, patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14).cuda() img_path = f'/kaggle/input/demo-image/1 (4).png' img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB') imgs_tensor[0] = transform(img)[:3] with torch.no_grad(): features_dict = dinov2_vitb14.forward_features(imgs_tensor) features = features_dict['x_norm_patchtokens'] features = features.reshape(4 * patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim).cpu() pca = PCA(n_components=3) pca.fit(features) pca_features = pca.transform(features) pca_features[:, 0] = (pca_features[:, 0] - pca_features[:, 0].min()) / (pca_features[:, 0].max() - pca_features[:, 0].min()) pca_features_fg = pca_features[:, 0] > 0.3 pca_features_bg = ~pca_features_fg b = np.where(pca_features_bg) pca.fit(features[pca_features_fg]) pca_features_rem = pca.transform(features[pca_features_fg]) for i in range(3): # transform using mean and std, I personally found this transformation gives a better visualization pca_features_rem[:, i] = (pca_features_rem[:, i] - pca_features_rem[:, i].mean()) / (pca_features_rem[:, i].std() ** 2) + 0.5 pca_features_rgb = pca_features.copy() pca_features_rgb[pca_features_fg] = pca_features_rem pca_features_rgb[b] = 0 pca_features_rgb = pca_features_rgb.reshape(4, patch_h, patch_w, 3) plt.imshow(pca_features_rgb[0][...,::-1]) plt.savefig('features.png') plt.show() plt.close()3.2 使用vit_l14的模型
patch_h = 75 patch_w = 50 feat_dim = 1024 transform = T.Compose([ T.GaussianBlur(9, sigma=(0.1, 2.0)), T.Resize((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.CenterCrop((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)), ]) dinov2_vitl14 = torch.hub.load('', 'dinov2_vitl14',source='local').cuda() features = torch.zeros(4, patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim) imgs_tensor = torch.zeros(4, 3, patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14).cuda() img_path = f'/kaggle/input/demo-image/1 (4).png' img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB') imgs_tensor[0] = transform(img)[:3] with torch.no_grad(): features_dict = dinov2_vitl14.forward_features(imgs_tensor) features = features_dict['x_norm_patchtokens'] features = features.reshape(4 * patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim).cpu() pca = PCA(n_components=3) pca.fit(features) pca_features = pca.transform(features) pca_features[:, 0] = (pca_features[:, 0] - pca_features[:, 0].min()) / (pca_features[:, 0].max() - pca_features[:, 0].min()) pca_features_fg = pca_features[:, 0] > 0.3 pca_features_bg = ~pca_features_fg b = np.where(pca_features_bg) pca.fit(features[pca_features_fg]) pca_features_rem = pca.transform(features[pca_features_fg]) for i in range(3): # transform using mean and std, I personally found this transformation gives a better visualization pca_features_rem[:, i] = (pca_features_rem[:, i] - pca_features_rem[:, i].mean()) / (pca_features_rem[:, i].std() ** 2) + 0.5 pca_features_rgb = pca_features.copy() pca_features_rgb[pca_features_fg] = pca_features_rem pca_features_rgb[b] = 0 pca_features_rgb = pca_features_rgb.reshape(4, patch_h, patch_w, 3) plt.imshow(pca_features_rgb[0][...,::-1]) plt.savefig('features.png') plt.show() plt.close()3.3 使用vit_g14的模型
patch_h = 75 patch_w = 50 feat_dim = 1536 transform = T.Compose([ T.GaussianBlur(9, sigma=(0.1, 2.0)), T.Resize((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.CenterCrop((patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14)), T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)), ]) dinov2_vitg14 = torch.hub.load('', 'dinov2_vitg14',source='local').cuda() features = torch.zeros(4, patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim) imgs_tensor = torch.zeros(4, 3, patch_h * 14, patch_w * 14).cuda() img_path = f'/kaggle/input/demo-image/1 (4).png' img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB') imgs_tensor[0] = transform(img)[:3] with torch.no_grad(): features_dict = dinov2_vitg14.forward_features(imgs_tensor) features = features_dict['x_norm_patchtokens'] features = features.reshape(4 * patch_h * patch_w, feat_dim).cpu() pca = PCA(n_components=3) pca.fit(features) pca_features = pca.transform(features) pca_features[:, 0] = (pca_features[:, 0] - pca_features[:, 0].min()) / (pca_features[:, 0].max() - pca_features[:, 0].min()) pca_features_fg = pca_features[:, 0] > 0.3 pca_features_bg = ~pca_features_fg b = np.where(pca_features_bg) pca.fit(features[pca_features_fg]) pca_features_rem = pca.transform(features[pca_features_fg]) for i in range(3): # transform using mean and std, I personally found this transformation gives a better visualization pca_features_rem[:, i] = (pca_features_rem[:, i] - pca_features_rem[:, i].mean()) / (pca_features_rem[:, i].std() ** 2) + 0.5 pca_features_rgb = pca_features.copy() pca_features_rgb[pca_features_fg] = pca_features_rem pca_features_rgb[b] = 0 pca_features_rgb = pca_features_rgb.reshape(4, patch_h, patch_w, 3) plt.imshow(pca_features_rgb[0][...,::-1]) plt.savefig('features.png') plt.show() plt.close()







发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。